The Key Laboratory of Advanced Forming and Manufacturing of the Ministry of Education, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, proposes an autonomous localization method for wall-climbing robots based on the combination of an external RGB-D camera and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU).
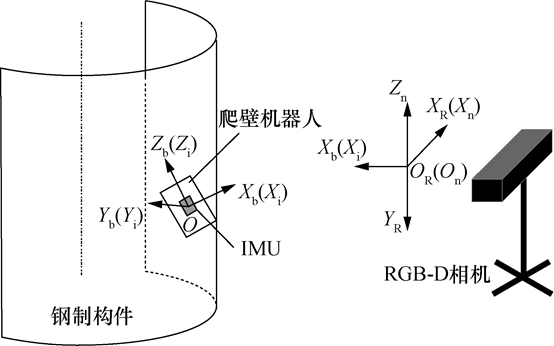
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of autonomous localization system for wall climbing robot
Climbing wall robot is widely used to complete the automatic flaw detection and cleaning of large steel components and other work, in the planning of the work route and the specified control strategy is, need to pass more climbing wall robot autonomous localization to obtain its own position on the surface of the steel components, and at the same time, according to the attitude of the climbing wall robot itself to adjust the operating probe in order to improve the efficiency of the work. However, in the existing robot autonomous localization methods, the face of storage tanks, diversion pressure steel pipe and other closed environments greatly limit the role of GPS in robot localization; at the same time, wall-climbing robots work on the surface of steel components, inevitably subject to magnetic interference, resulting in the role of the magnetic intensity meter in the estimation of the attitude is limited.
Aiming at the problem of limited sensor applications in closed environments, magnetic interference and other special scenarios, which leads to the accumulation of autonomous localization errors of wall-climbing robots over time, the Key Laboratory of Advanced Forming and Manufacturing of the Ministry of Education, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University, proposes and realizes an autonomous localization method for wall-climbing robots based on the combination of an external RGB-D camera and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU). A wall climbing robot autonomous localization method based on the combination of external RGB-D camera and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is proposed and realized.
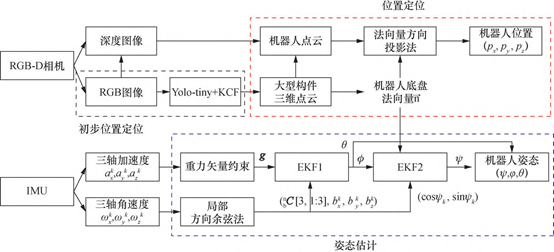
The method adopts a combination of deep learning and Kernelized Correlation Filter (KCF) target tracking method for preliminary position localization; based on this, the centroid of the top of the robot chassis is filtered out using the method of normal vector directional projection, and the positional localization of the wall-climbing robot is realized. The quantitative relationship between the normal vector of the robot chassis, the traverse angle and the heading angle is deduced, and the series-connected Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) is designed to compute the traverse angle, the pitch angle and the heading angle to realize the attitude estimation in robot localization.
Fig. 2 Block diagram of RGB-D + IMU autonomous localization method structure
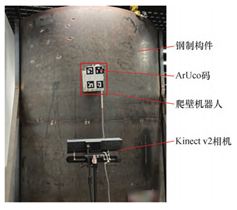
The Tsinghua team used a 0.25m long, 0.19m wide, 0.27m high steel component wall-climbing robot for experimental validation, the RGB-D camera was Microsoft Kinectv2 and the IMU was ADIS16445. the object is shown in Fig:
Fig. 3 Physical diagram of RGB-D + IMU autonomous localization method
The experimental results show that: the positional localization error of the wall-climbing robot decreases from 0.18m to about 0.02m; the heading angle error and the traverse roll angle error are less than 2.5°, and the pitch angle error is less than 1.5°, which effectively improves the wall-climbing robot's localization accuracy. When the working range of the robot exceeds the maximum field of view of a single RGB-D camera, the field of view can be expanded by combining multiple RGB-D cameras.
Fig. 4 Experimental results of RGB-D + IMU autonomous localization method